Boost Angular App Speed Using the Defer Feature
Angular's defer feature is a game-changer for performance. Learn how it works and how to implement it to speed up your apps significantly. Download full source code.
Error management reduces the risk of leak of crucial information to users. Centralized logging provides efficient monitoring, debugging, and forensic analysis. In angular applications nowadays, secure logging and robust error handling are required to maintain the stability, making the detection of security threats and user data's protection in angular application. Angular has some built-in protections from vulnerabilities attacks in web-application like XSS, input validation and Sanitization.
Node.js v20.19.2
Angular cli v18.2.20
Before we begin, ensure Node.js and Angular CLI is installed.
Run the following command to generate a new Angular app and use strict flag to reduce security mistakes and improve type safety.
Run ‘ng new best-security-practices --strict ‘
To open directory run change directory command
Run ‘cd best-security-practices‘
After creation serve the project using command
Run ‘npm start or ng serve’
By default, Angular includes sample HTML in the AppComponent. To prepare for a routed layout:
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
This enables Angular’s router to display components based on the current route.
Use Angular CLI commands to scaffold the necessary components. Open a terminal in your project directory and run the following:
Run ‘ng g c layout’
Run ‘ng g c layout/header’
Run ‘ng g c layout/footer’
These components will be used to structure your application page and layout.
Now create components for login and page-not-found page. And Components for home, about, dashboard in user directory.
Run ‘ng g c login’
Run ‘ng g c page-not-found’
Run ‘ng g c user/home’
Run ‘ng g c user/about’
Run ‘ng g c user/dashboard’
Update your app.routes.ts file to define application routes by implementing nested routes.
import { Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { LayoutComponent } from './layout/layout.component';
import { HomeComponent } from './user/home/home.component';
import { DashboardComponent } from './user/dashboard/dashboard.component';
import { PageNotFoundComponent } from './page-not-found/page-not-found.component';
import { LoginComponent } from './login/login.component';
import { AboutComponent } from './user/about/about.component';
export const routes: Routes = [
{path:'', redirectTo:'/user/home', pathMatch:'full'},
{path:'user', component:LayoutComponent, children:[
{path:'home', component:HomeComponent},
{path:'about', component:AboutComponent},
{path:'dashboard', component:DashboardComponent}
]},
{path:'login', component:LoginComponent},
{path:'**', component:PageNotFoundComponent}
];
Add Bootstrap v5.3 using CDN links add these tags to attach css and javascript bundle files in index.html.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>BestSecurityPractices</title>
<base href="/">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico">
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-LN+7fdVzj6u52u30Kp6M/trliBMCMKTyK833zpbD+pXdCLuTusPj697FH4R/5mcr" crossorigin="anonymous">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap-icons@1.13.1/font/bootstrap-icons.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.7/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha384-ndDqU0Gzau9qJ1lfW4pNLlhNTkCfHzAVBReH9diLvGRem5+R9g2FzA8ZGN954O5Q" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</body>
</html>
Now let’s start working on the layout design of the project in layout.component.html. Add component selector of header component and footer component and router-outlet.
In the layout component add the class HeaderComponent, FooterComponent and RouterOutlet in the imports array.
<app-header></app-header>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
<app-footer></app-footer>
Let’ add in the header component, a navbar is created with links for home, about and login page. Also, add Routerlink in the imports array in header.component.ts.
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg bg-body-tertiary">
<div class="container">
<a class="navbar-brand" routerLink="/user/home">Project</a>
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-bs-toggle="collapse" data-bs-target="#navbarSupportedContent"
aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarSupportedContent">
<ul class="navbar-nav me-auto mb-2 mb-lg-0">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" aria-current="page" routerLink="/user/home" routerLinkActive="active">Home</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" routerLink="/user/about" routerLinkActive="active">About</a>
</li>
</ul>
<div class="d-flex">
<button class="btn btn-outline-primary" type="button" routerLink="/login">Login</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
Next is the home component, Create a banner for the project in the home.component.html
<div class="home">
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-6">
<p class="fs-1 fw-bold">Best Practices for securing Angular Application</p>
<button class="btn btn-outline-primary" routerLink="/user/about">Get Started</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Add this to home.component.css to add styling.
.home{
padding: 100px 0;
background-image: url(/images/1.jpg);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}
Next is add a card in the footer component, in footer.component.html. Add Class RouterLink in the imports array.
<div class="card text-center">
<div class="card-header">
<div class="container">
Error management reduces the risk of leak of crucial information to users. Centralized logging provides efficient monitoring, debugging, and forensic analysis. In angular applications nowadays, secure logging and robust error handling are required to maintain the stability, making the detection of security threats and user data's protection in angular application. Angular has some built-in protections from vulnerabilities attacks in web-application like XSS, input validation and Sanitization.
</div>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">Best Security Practices</h5>
<p class="card-text">Different practices and strategies are available to secure the angular application.</p>
<a routerLink="/login" class="btn btn-primary">Login</a>
</div>
<div class="card-footer text-body-secondary">
<i class="bi bi-c-circle"></i> Copyrights
</div>
</div>
Create a form in the login component. Add this code in login.component.html and add class RouterLink in the imports array in login.component.ts
<div class="login py-5">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-12">
<h4 class="text-center">Login</h4>
<nav style="--bs-breadcrumb-divider: '>';" class="" aria-label="breadcrumb">
<ol class="breadcrumb justify-content-center">
<li class="breadcrumb-item"><a routerLink="/user/home">Home</a></li>
<li class="breadcrumb-item active" aria-current="page">Login</li>
</ol>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-md-3"></div>
<div class="col-md-6 p-5 bg-secondary-subtle rounded-5">
<form>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1" class="form-label">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp"
formControlName="email">
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1" class="form-label">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1"
formControlName="password">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" >Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="col-md-3"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Add this styling for login form in login.component.css.
.login{
height: 100vh;
background-image: url(/images/1.jpg);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}
The preview of login page is as follows:
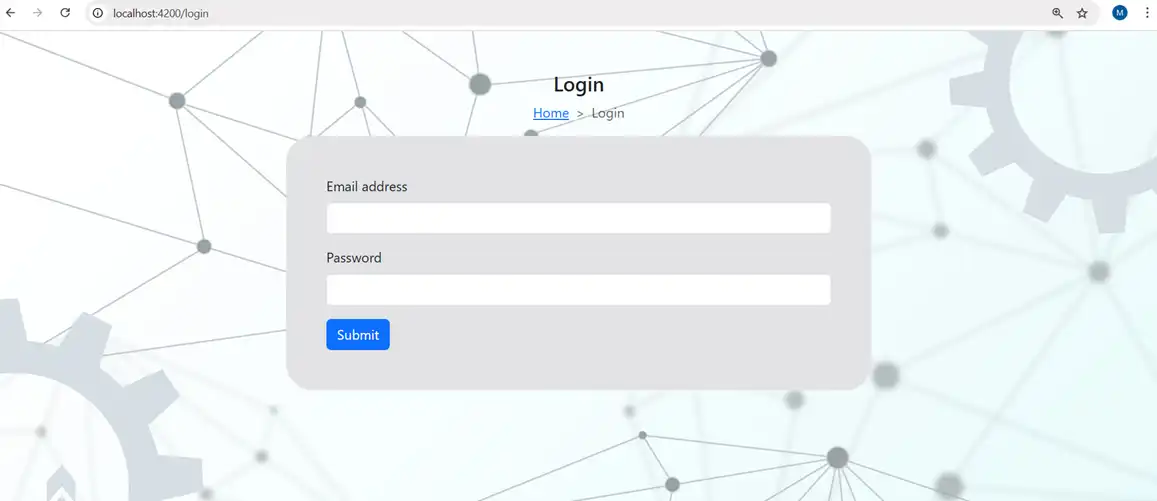
Securing an angular app with the best practices are mentioned below.
To ensure that data meets the rules for inputs, validations are added to code. Here validation is added to login form created using reactive form and validators in it, a custom password regex is used as pattern validator. First in login.component.ts reactive form with validation by importing ReactiveFormsModule and NgIf in imports array. Create a function named loginFun to login form submission.
loginForm = new FormGroup({
email:new FormControl("", [Validators.required, Validators.email]),
password:new FormControl("", [Validators.required, Validators.pattern(/^(?=[^A-Z]*[A-Z])(?=[^a-z]*[a-z])(?=\D*\d).{8,}$/)])
})
loginFun(){}
Changes in form in login.component.html are as follows
<form [formGroup]="loginForm" (submit)="loginFun()">
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1" class="form-label">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" formControlName="email">
@if(loginForm.controls['email'].touched && loginForm.controls['email'].errors?.['required']){
<div class="form-text text-danger">Email is required</div>
}
@if(loginForm.controls['email'].touched && loginForm.controls['email'].errors?.['email']){
<div class="form-text text-danger">Invalid Email</div>
}
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1" class="form-label">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" formControlName="password">
@if(loginForm.controls['password'].touched && loginForm.controls['password'].errors?.['required']){
<div class="form-text text-danger">Password is required</div>
}
@if(loginForm.controls['password'].touched && loginForm.controls['password'].errors?.['pattern']){
<div class="form-text text-danger">Invalid Password ( Password should have a minimum 8 characters, at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one number and one special character )</div>
}
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" [disabled]="loginForm.invalid">Submit</button>
</form>
To perform authentication using login form let’s create an auth service first and create functions for login to store token and user details in session storage, logout to navigate and clear the session storage. A getToken function which returns the token. A getRole that returns the role.
Run this command to create an auth service.
Run ‘ng g s services/auth’
Also install ngx-toastr to the project to show popup messages to users
Add the provider for toasts and animations in app.config.ts
providers: [
provideZoneChangeDetection({ eventCoalescing: true }),
provideRouter(routes),
provideAnimations(),
provideToastr({
preventDuplicates:true,
positionClass:'toast-bottom-center'
})
]
In angular.json add the css path and restart the app.
"styles": [
"src/styles.css",
"node_modules/ngx-toastr/toastr.css"
],
Add this code in auth.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import { ToastrService } from 'ngx-toastr';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class AuthService {
constructor(private router:Router, private toastr:ToastrService) { }
login(info:any){
sessionStorage.setItem('token', 'true')
sessionStorage.setItem('email', info.email)
sessionStorage.setItem('name', info.name)
sessionStorage.setItem('role', info.role)
this.router.navigateByUrl('/user/home')
}
logout(){
sessionStorage.clear()
this.router.navigateByUrl('/login')
this.toastr.success("Logged out successfully")
}
getToken(){
return sessionStorage.getItem('token')
}
getRole(){
return sessionStorage.getItem('role')
}
}
Create an instance of auth service in login.component.ts and use it in the login function. Email and Password will be matched using a comparison operator.
constructor(private auth:AuthService, private toastr:ToastrService){
loginFun(){
let credentials = this.loginForm.value
if(credentials.email == 'user@gmail.com' && credentials.password == 'Qwerty@123'){
let info:any = {
email:credentials.email,
name:'John',
role:'user'
}
this.auth.login(info)
this.toastr.success("Login Successful")
}
else{
this.toastr.error("Incorrect Credentials")
}
}
Next is to add functionality after login in the header. In header.component.html add a button for logout and a dropdown in case the user is logged in to show pages like dashboard and other functionality which is only shown after login. After logout hide this drop down and logout button.
<div class="d-flex">
@if (isLoggedIn) {
<div class="dropdown">
<button class="btn btn-primary dropdown-toggle me-4" type="button" data-bs-toggle="dropdown"
aria-expanded="false">
{{name}}
</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a class="dropdown-item" routerLink="/user/dashboard">Dashboard</a></li>
<li><a class="dropdown-item" routerLink="">Action Center</a></li>
<li><a class="dropdown-item" routerLink="">Manage Passwords</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
}
@if(isLoggedIn){
<button class="btn btn-outline-primary" type="button" (click)="logout()">Logout</button>
}
@else{
<button class="btn btn-outline-primary" type="button" routerLink="/login">Login</button>}
</div>
In header.component.ts a flag is added isLoggedIn to check if the user is logged in or not and show the login or logout button accordingly. The name variable to show the user's name on the dropdown. A logout function.
name:string = ''
isLoggedIn:boolean = false
constructor(private auth:AuthService){}
ngOnInit(): void {
if(!!this.auth.getToken()){
this.isLoggedIn = true
this.name = sessionStorage.getItem('name') ?? ''
}
else{
this.name = ""
this.isLoggedIn = false
}
}
logout(){
this.auth.logout()
}
The dashboard page is not shown if the user has not logged in and after logout. But it can be accessed using routes, to authorise some functionality only to authenticated users we can implement roles and route guards. By this we can protect routes for admin and restricted roles. Guards canActivate, canLoad, canActivateChild can be used. Avoid exposing sensitive data view route parameters. For that create a route guard using the command
Run ‘ng g g guards/user-auth’
Choose CanActivate guard to be created.
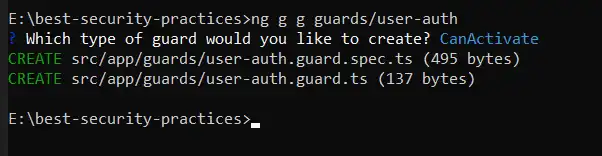
Add the code in user-auth.guard.ts
import { inject } from '@angular/core';
import { CanActivateFn, Router } from '@angular/router';
import { AuthService } from '../services/auth.service';
export const userAuthGuard: CanActivateFn = (route, state) => {
let auth = inject(AuthService)
let router = inject(Router)
if(!!auth.getToken() && auth.getRole()=='user'){
return true;
}
else{
router.navigateByUrl('/user/home')
return false
}
};
Use this guard in app.routes.ts to protect the pages
{path:'user', component:LayoutComponent, children:[
{path:'home', component:HomeComponent},
{path:'about', component:AboutComponent},
{path:'dashboard', component:DashboardComponent, canActivate:[userAuthGuard]}
]},
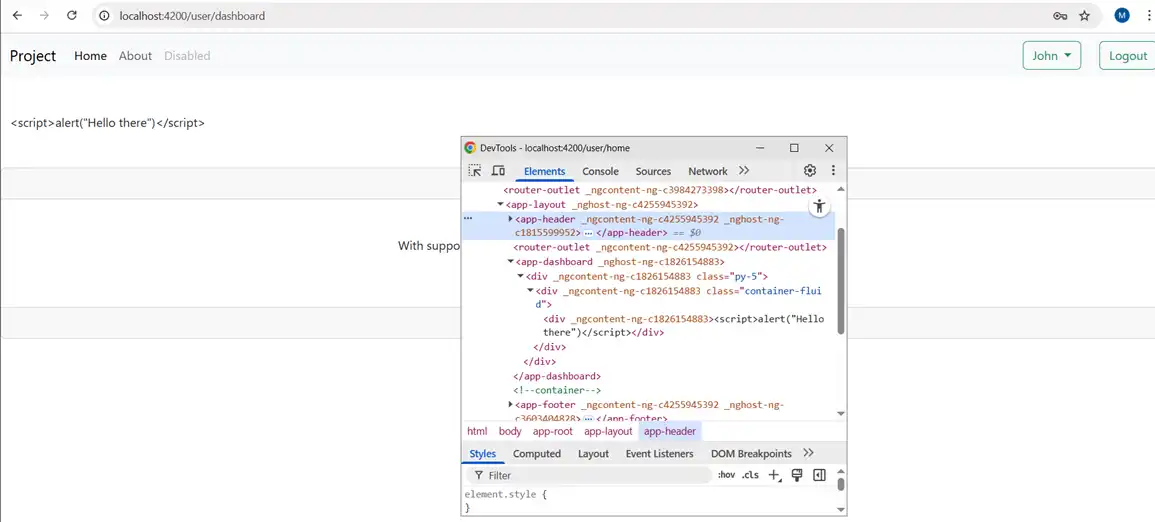
Attackers can add malicious code from entering DOM and steal user login information using cross-site scripting by adding script tag into user input, onerror in img tag and href in anchor tag. Angular treats all values untrusted and are sanitized on entering DOM using template binding. Let’s see how to implement built-in sanitization techniques in angular. Here are the examples.
Here in interpolation the content is escaped and the browser displays angle brackets as text. Binding into a value that an attacker can add causes XSS vulnerability. Avoid using innerHTML and be careful while using third-party libraries and check dynamic style or class bindings for user-controlled input.
<div class="py-5">
<div class="container">
<div class="my-3">{{alertMessage}}</div>
</div>
</div>
alertMessage: any
constructor() {
this.alertMessage = '<script>alert("Hello there")</script>'
}
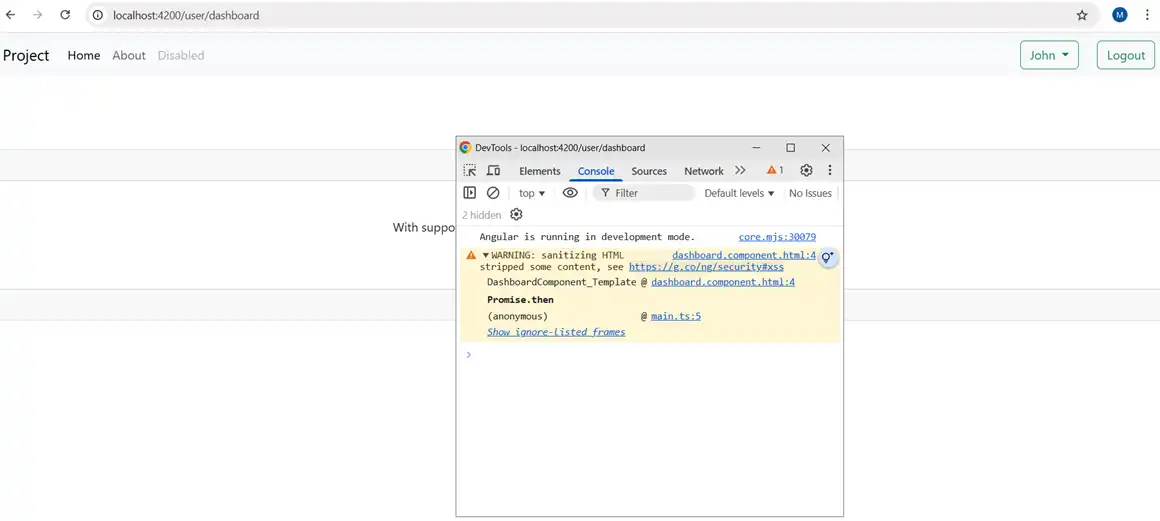
Avoid innerHTML and use angular’s data binding. Do not trust user input , validate it and use DomSanitizer for sanitizing.
<div class="py-5">
<div class="container">
<!-- <div class="my-3"> {{alertMessage}}</div> -->
<div class="my-3" [innerHTML]="alertMessage"> </div>
</div>
</div>
For sanitizing text, from methods of DomSanitizer, bypassSecurityTrustHtml can be used.
<div class="py-5">
<div class="container">
<!-- <div class="my-3">{{alertMessage}}</div> -->
<!-- <div class="my-3" [innerHTML]="alertMessage"> </div> -->
<div class="my-3" [innerHTML]="safeText"></div>
</div>
</div>
alertMessage: any
safeText: SafeHtml
constructor(private sanitizer: DomSanitizer) {
this.alertMessage = '<script>alert("Hello there")</script>'
this.safeText = sanitizer.bypassSecurityTrustHtml(this.alertMessage)
}
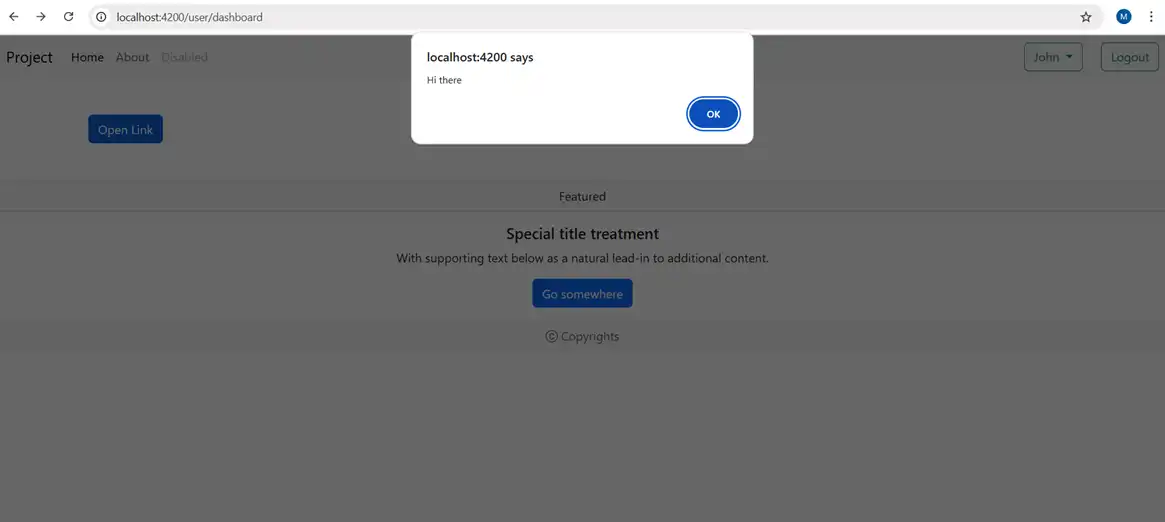
Hyperlinks: As angular automatically sanitizes the URL and disables dangerous code and logs errors in code, to remove this URL can be used with bypassSecurityTrustUrl can be used.
<div class="py-5">
<div class="container">
<div class="my-3">
<!-- <a class="btn btn-primary" [href]="href"> Open Alert</a> -->
<a class="btn btn-primary" [href]="safeUrl">Open Alert</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
href: any
safeUrl: SafeUrl
constructor(private sanitizer: DomSanitizer) {
this.href = "javascript:alert('Hello there')"
this.safeUrl = sanitizer.bypassSecurityTrustUrl(this.href)
}
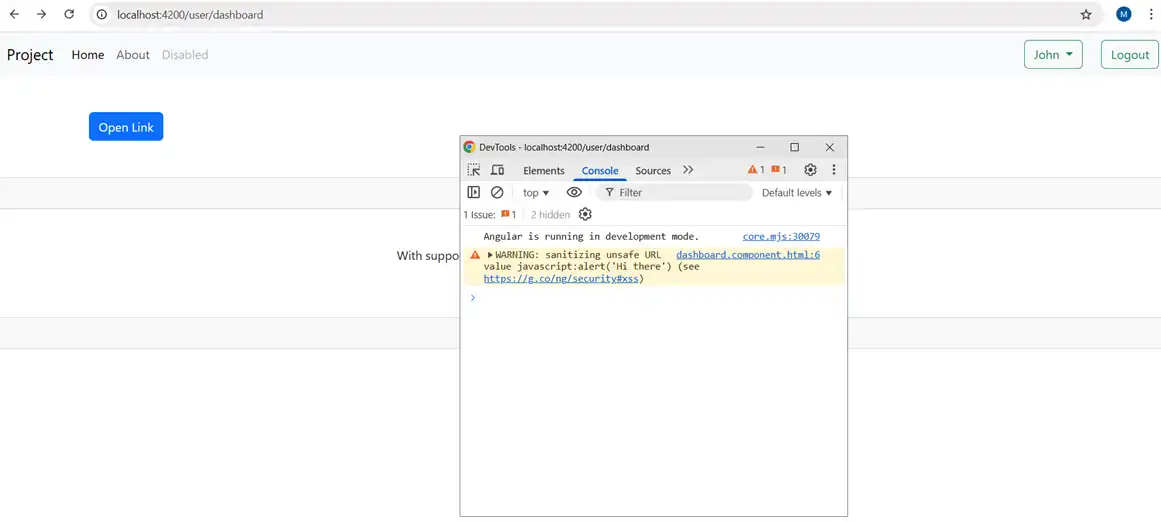
This is how it works
Resource Url: Here an untrusted can smuggle in file downloads that unsuspecting users can run.
<div class="py-5">
<div class="container">
<div class="my-3">
<!-- <iframe width="560" height="315" [src]="videoSrc" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe> -->
<iframe width="560" height="315" [src]="safeVideoSrc" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0"
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share"
referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe>
</div>
</div>
</div>
videoSrc: any
safeVideoSrc: SafeResourceUrl
constructor(private sanitizer: DomSanitizer) {
this.videoSrc = "https://www.youtube.com/embed/FpivELteI-0?si=PI1-HJRkuuTD29H6"
this.safeVideoSrc = sanitizer.bypassSecurityTrustResourceUrl(this.videoSrc)
}
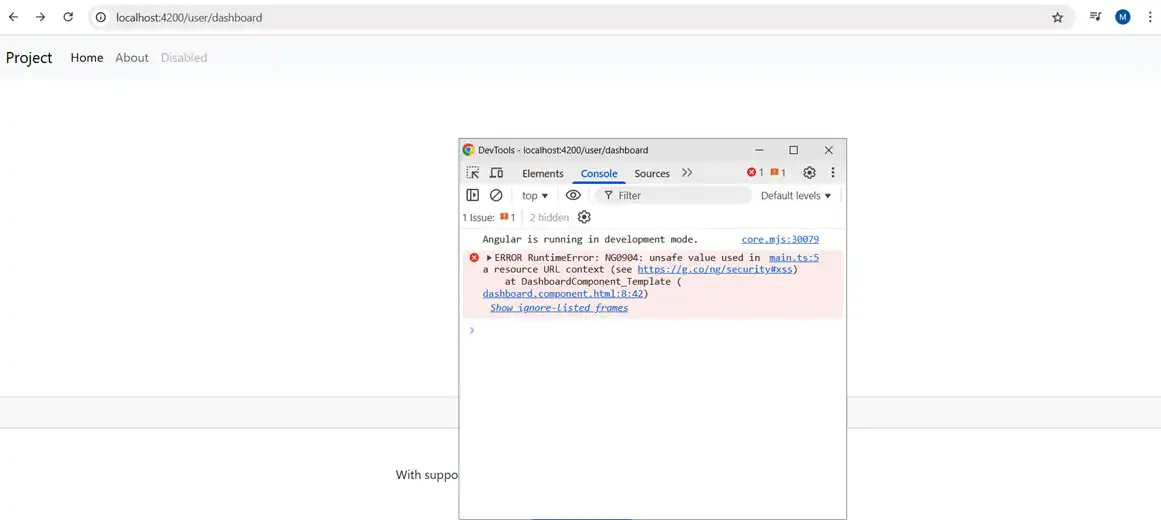
It is necessary to use HTTPS for API calls. Validate and sanitize input on the server. Use Angular built-in HttpClient with interceptors for token management. Also for the server, set proper CORS policies.
Create Interceptor named auth using the command
Run ‘ng g interceptor interceptors/auth’
Add this into the code
import { HttpInterceptorFn } from '@angular/common/http';
import { inject } from '@angular/core';
import { AuthService } from '../services/auth.service';
export const authInterceptor: HttpInterceptorFn = (req, next) => {
let auth:any = inject(AuthService)
let token = auth.getToken()
if(token){
req = req.clone({
headers:req.headers.set('Authorization', `Bearer ${token}`)
})
}
return next(req);
};
Add the provider for interceptor
provideHttpClient(
withInterceptors([authInterceptor]),
),
Create a dashboard service using the following command and create a function getDashboard which calls an API using HttpClient.
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class DashboardService {
constructor(private http:HttpClient) { }
getDashboard(){
return this.http.get('/api/getDashboard')
}
}
Cross-Site Request Forgery means for example an attacker tricks your logged-in user’s browser to send a request (like “delete account”, “transfer money”) to your server, re-using the user’s credentials (cookies) without the user’s consent.
Angular itself doesn’t generate CSRF tokens because that’s a server concernCS RF can be handled by enabling server-side CSRF tokens.
provideHttpClient(
withInterceptors([authInterceptor]),
withXsrfConfiguration({
cookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN',
headerName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN'
})
),
Content Security Policy (CSP) is an HTTP response header that tells the browser what scripts are allowed to run, what styles can be loaded and what images can be loaded. It is the single strongest defense against XSS. CSP protects you before any JavaScript is parsed.
Create error handler in angular application by creating a file named error-handler.ts in app/handler directory.
import { ErrorHandler, Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable()
export class errorHandler implements ErrorHandler {
handleError(error: any): void {
console.log("Error occurred =", error)
alert("Something went wrong, Try Again")
}
}
Add its provider in app.config.ts
{provide:ErrorHandler, useClass:errorHandler},
In Dashboard Component create a function getData and create instance of Dashboard Service and a variable named errorMessage
getData() {
this._dashboard.getDashboard().subscribe({
next: (data:any) => { /* handle success */ },
error: () => {
this.errorMessage = "Some error occurred. Please try again later.";
}
});
}
By combining all these practices to safe the userdata by authentication, authorization, using HTTPS for encrypting communication, sanitizing user inputs, robust CSP, we can create the angular application would be consistent in error handling for all features, will have minimal exposure to sensitive technical information, a mechanism to analyze errors used to proactively protect the angular application.
Angular's defer feature is a game-changer for performance. Learn how it works and how to implement it to speed up your apps significantly. Download full source code.
Learn top strategies to secure Angular applications. Explore best practices for authentication, data protection, API security, and code vulnerability checks.
Explore how Zone.js powers change detection in Angular apps. This comprehensive guide covers how it works, use cases, performance tips, and advanced debugging.
Learn how to build modern full stack applications using Angular and ASP.NET Core. Explore architecture, API integration, deployment tips, and best practices.
Learn how to implement Azure AD authentication in your Angular app using MSAL and connect it securely with ASP.NET Core Web API. Step-by-step setup included.
Dive into Angular 20's latest updates, trending features, performance boosts, and tools reshaping frontend development. All in one detailed, easy-to-read guide.
Get in touch with Prishusoft – your trusted partner for custom software development. Whether you need a powerful web application or a sleek mobile app, our expert team is here to turn your ideas into reality.
